Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease. It causes obstruction and narrowing of the respiratory tract due to prolonged damage to the respiratory system, and makes it hard to breathe. It develops as a significant and chronic inflammatory response to inhaled irritants including Chronic bronchitis, Bronchiectasis and Emphysema.
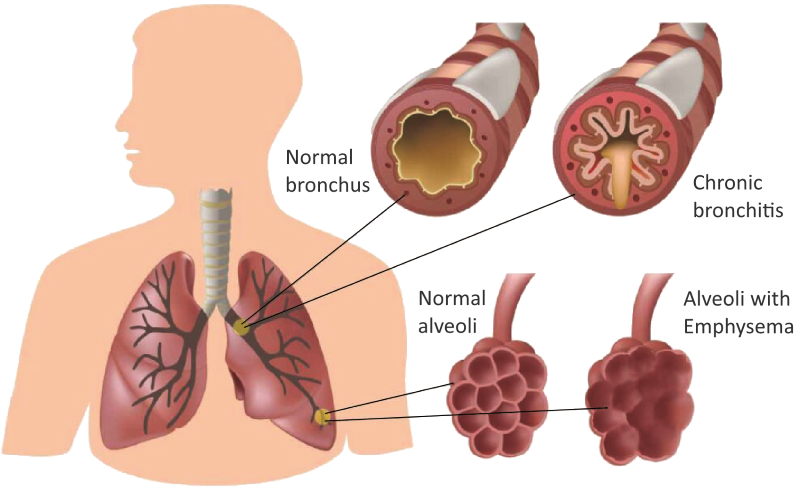
In the early stages of COPD, there may be no symptoms or symptoms can be quite mild, beginning with coughing and shortness of breath. As it progresses, it can get progressively worse and become increasingly difficult to breathe. Following are the main symptoms of COPD:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) occurs when the lungs and respiratory tract become damaged and inflamed. It is usually associated with long-term exposure to substances that irritate and damage the lungs. The main causes may include:
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) develops slowly but can cause many complications, they include:
1. Smoking cessation and avoid secondhand smoke
Unlike some diseases, COPD has a clear cause which cigarette smoking is the main cause of the disease. Smoking cessation can effectively reduce the patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease cough and sputum, can also delay the deterioration of the disease. Also, stay away from secondhand smoke which can increase the risk of COPD.
2. Occupational health
Wear suitable respiratory protective equipment. such as a mask to prevent dust exposure.
3. Exercise regularly
Regular exercise can help to enhance personal physique in order to enhance immunity.
COPD has no cure yet, and doctors do not have any ways to repair the damage to the lungs. However, suitable treatments and lifestyle changes can help patients to ease symptoms, control the disease and reduce the risk of complications.
Medications, oxygen therapy, and surgery are some forms of treatment.